Intro to Deep Learning and Computer Vision
对卷积神经网络的一个直观印象:
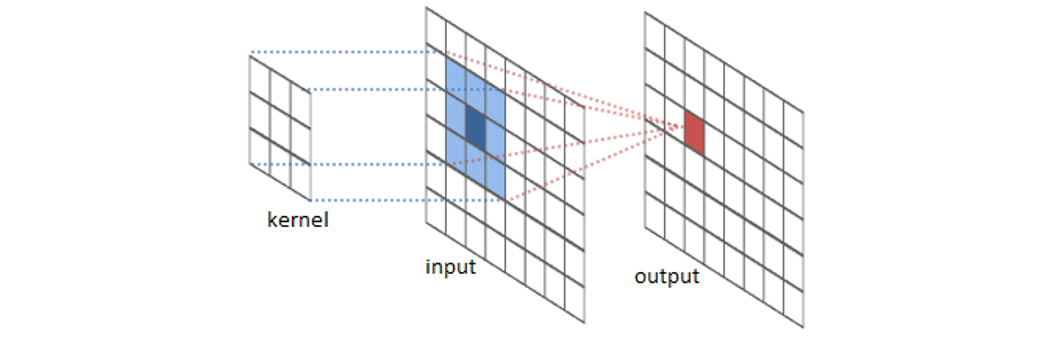
Programming in TensorFlow and Keras
下面是一个卷积的例子:
# Function to Read and Prep Images for Modeling
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.python.keras.applications.resnet50 import preprocess_input
from tensorflow.python.keras.preprocessing.image import load_img, img_to_array
image_size = 224
def read_and_prep_images(img_paths, img_height=image_size, img_width=image_size):
imgs = [load_img(img_path, target_size=(img_height, img_width)) for img_path in img_paths]
img_array = np.array([img_to_array(img) for img in imgs])
return preprocess_input(img_array)
# Create Model with Pre-Trained Weights File. Make Predictions
from tensorflow.python.keras.applications import ResNet50
my_model = ResNet50(weights='../input/resnet50/resnet50_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels.h5')
test_data = read_and_prep_images(img_paths)
preds = my_model.predict(test_data)
# Visualize Predictions
import sys
# Add directory holding utility functions to path to allow importing
sys.path.append('/kaggle/input/python-utility-code-for-deep-learning-exercises/utils')
from decode_predictions import decode_predictions
from IPython.display import Image, display
most_likely_labels = decode_predictions(preds, top=3, class_list_path='../input/resnet50/imagenet_class_index.json')
for i, img_path in enumerate(img_paths):
display(Image(img_path))
print(most_likely_labels[i])
Transfer Learning
下面是迁移学习的例子:
# Specify Model
from tensorflow.python.keras.applications import ResNet50
from tensorflow.python.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.python.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, GlobalAveragePooling2D
num_classes = 2
resnet_weights_path = '../input/resnet50/resnet50_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5'
my_new_model = Sequential()
my_new_model.add(ResNet50(include_top=False, pooling='avg', weights=resnet_weights_path))
my_new_model.add(Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax'))
# Say not to train first layer (ResNet) model. It is already trained
my_new_model.layers[0].trainable = False
# Compile Model
my_new_model.compile(optimizer='sgd', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
# Fit Model
from tensorflow.python.keras.applications.resnet50 import preprocess_input
from tensorflow.python.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
image_size = 224
data_generator = ImageDataGenerator(preprocessing_function=preprocess_input)
train_generator = data_generator.flow_from_directory(
'../input/urban-and-rural-photos/rural_and_urban_photos/train',
target_size=(image_size, image_size),
batch_size=24,
class_mode='categorical')
validation_generator = data_generator.flow_from_directory(
'../input/urban-and-rural-photos/rural_and_urban_photos/val',
target_size=(image_size, image_size),
class_mode='categorical')
my_new_model.fit_generator(
train_generator,
steps_per_epoch=3,
validation_data=validation_generator,
validation_steps=1)
Data Augmentation
下面是数据增强的例子:
from tensorflow.python.keras.applications.resnet50 import preprocess_input
from tensorflow.python.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
image_size = 224
data_generator_with_aug = ImageDataGenerator(preprocessing_function=preprocess_input,
horizontal_flip=True,
width_shift_range = 0.2,
height_shift_range = 0.2)
train_generator = data_generator_with_aug.flow_from_directory(
'../input/urban-and-rural-photos/rural_and_urban_photos/train',
target_size=(image_size, image_size),
batch_size=24,
class_mode='categorical')
data_generator_no_aug = ImageDataGenerator(preprocessing_function=preprocess_input)
validation_generator = data_generator_no_aug.flow_from_directory(
'../input/urban-and-rural-photos/rural_and_urban_photos/val',
target_size=(image_size, image_size),
class_mode='categorical')
my_new_model.fit_generator(
train_generator,
steps_per_epoch=3,
epochs=2,
validation_data=validation_generator,
validation_steps=1)
Deep Learning From Scratch
一个从头搭建卷积网络的例子:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from tensorflow.python import keras
from tensorflow.python.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.python.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv2D, Dropout
img_rows, img_cols = 28, 28
num_classes = 10
def data_prep(raw):
out_y = keras.utils.to_categorical(raw.label, num_classes)
num_images = raw.shape[0]
x_as_array = raw.values[:,1:]
x_shaped_array = x_as_array.reshape(num_images, img_rows, img_cols, 1)
out_x = x_shaped_array / 255
return out_x, out_y
train_file = "../input/digit-recognizer/train.csv"
raw_data = pd.read_csv(train_file)
x, y = data_prep(raw_data)
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(20, kernel_size=(3, 3),
activation='relu',
input_shape=(img_rows, img_cols, 1)))
model.add(Conv2D(20, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(128, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax'))
model.compile(loss=keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy,
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(x, y,
batch_size=128,
epochs=2,
validation_split = 0.2)
Dropout and Strides For Larger Models
Dropout用于应对过拟合,Stride lengths让模型运算更快,内存消耗更少:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from tensorflow.python import keras
from tensorflow.python.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.python.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv2D, Dropout
img_rows, img_cols = 28, 28
num_classes = 10
def data_prep(raw):
out_y = keras.utils.to_categorical(raw.label, num_classes)
num_images = raw.shape[0]
x_as_array = raw.values[:,1:]
x_shaped_array = x_as_array.reshape(num_images, img_rows, img_cols, 1)
out_x = x_shaped_array / 255
return out_x, out_y
train_size = 30000
train_file = "../input/digit-recognizer/train.csv"
raw_data = pd.read_csv(train_file)
x, y = data_prep(raw_data)
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(30, kernel_size=(3, 3),
strides=2,
activation='relu',
input_shape=(img_rows, img_cols, 1)))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Conv2D(30, kernel_size=(3, 3), strides=2, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(128, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax'))
model.compile(loss=keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy,
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(x, y,
batch_size=128,
epochs=2,
validation_split = 0.2)

